IPsec Tunnels
CONFIGURE > NETWORK CONNECTIONS > IPsec Tunnels
The Opengear Console Manager (CM) can use IPsec to securely connect and route between two or more LANs (sometimes referred to as site to site, LAN-to-LAN, L2L VPN), or as a single client endpoint connecting to a central LAN or endpoint (sometimes referred to as host to site, or host to host).
IPsec does not make a formal distinction between initiator and responder, however the Opengear CM can both initiate tunnels (as the "initiator") and have other devices initiate tunnels to it (as a "responder").
Create, Add or Edit IPsec Tunnels
On the IPsec Tunnels page, you can create, edit, and delete IPsec tunnels.
To create an IPsec tunnel:
-
Click CONFIGURE > NETWORK CONNECTIONS > IPsec Tunnels.
The IPsec Tunnels page with two tunnels previously created.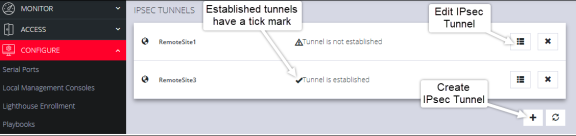
If there are no existing tunnels, this Create Tunnel button is displayed: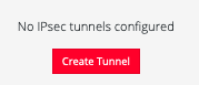
-
Click CREATE TUNNEL. This opens the EDIT IPSEC TUNNEL page.
NAME and STATUS
-
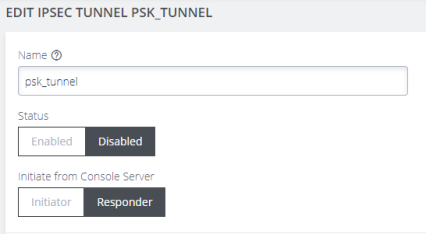
In the Name section of the page, give your new tunnel a unique name and click the Enabled button.
-
Set the Console Server to be the Initiator or Responder.
Note:When Initiatoris selected, the node will actively initiate the tunnel by sending IKE negotiation packets to the remote end.
IKE SETTINGS
Continued...
-
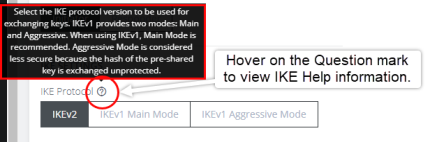
Select an IKE Protocol version to use for exchanging keys. IKEv1 provides two modes: Main and Aggressive. When using IKEv1, Main Mode is recommended. Aggressive Mode is considered less secure because the hash of the pre-shared key is exchanged unprotected.
-
Select the Algorithm Proposal. This is a set of algorithms used for negotiation when attempting to establish the IPsec tunnel. By default, the node will attempt to negotiate the tunnel using a list of common algorithms which are considered safe. Alternatively, a set of default proposals that guarantee Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) can be selected.
-
Select Initiate to actively initiate the tunnel by sending IKE negotiation packets to the remote end.
-
Set up the Phase 1 and Phase 2 time interval between the key material refresh of the IKE and Child.
AUTHENTICATION
CM Authentication can use PSK or PKI.
-
For pre-shared key (PSK) authentication, enter a pre-shared secret key; both ends of the tunnel must use the same key.
Tip:
To construct ID_USER_FQDN identities, use user@example.com
To construct ID_FQDN type identities, use @host.example.com
If left blank, the outer local IP address of the tunnel is used as the identity. -
Enter a Local ID Identity or IP address for the local end of the tunnel. If left blank, the outer-local IP address is used as the source address of the tunnel.
-
For Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) authentication, upload the certification bundle file or, drag and drop the file into the Certificate Bundle field.
TUNNEL SETTINGS
-
Select Enabled if enforced UDP encapsulation is required. When enabled, the IKE daemon can simulate the NAT detection payload.
ADDRESSING
-
Enter the Local Address to be used as the source address of the tunnel. If left blank, IPsec will automatically use a default.
-
Enter a Local Subnet. Specify local traffic to be tunneled. When no subnets are specified, only traffic originating from this device will be tunneled.
-
Enter the Remote Address or hostname for the remote end of the tunnel. If left blank, IPsec will accept initiation packets from any address.
-
Enter the Remote Subnet. Specify addresses or subnets that are behind the remote end of this tunnel. If no subnet is specified, only traffic originating from the outer remote address will be accepted.
DEAD PEER DETECTION
Tip: Dead Peer Detection may be used to support long-lived tunnels.
Dead Peer Detection (DPD) is a method used by nodes to verify the current existence and availability of IPsec peers. A node performs this verification by sending encrypted IKE Phase 1 notification payloads (R-U-THERE messages) to a peer and waiting for DPD acknowledgments (R-U-THERE-ACK messages) from the peer.
Continued...
You can enable DPD and configure the various options to fine-tune the functionality:
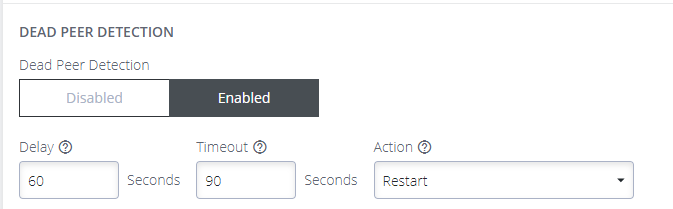
-
Delay - the time interval between polling the peer (default is 60 seconds).
-
Timeout - the waiting time before deciding that a peer connection is not live (default is 90 seconds).
-
Action - the action to be performed when a connection is timed-out. (default is Restart).
-
Restart will immediately attempt to renegotiate the tunnel.
-
Clear will close the CHILD_SA.
-
Trap will catch matching traffic.
-
ENABLE the IPsec TUNNEL
-
When you have completed the IPsec Tunnel set-up process, ensure the IPsec tunnel status is set to Enabled, then, click Save.
The new tunnel is now listed on the CONFIGURE > NETWORK CONNECTIONS > IPsec Tunnels page.